
Lecture Three: Type of Signalling
This lecture aims to provide insight into signaling pathways and their respective examples. There are four main signaling pathways: Paracrine, contact-dependent, autocrine, and endocrine signaling which vary based on the distance traveled to reach the target cells. Each signaling pathway consists of three main steps: activation of receptors, signal transduction, and cellular response. Activation of receptors involves a stimulus or a signal that can influence the properties of the cell. Each receptor is a type of protein that can bind specifically to its complementary signaling molecule called a ligand on its target cells. Just like a lock and key model.
Signal transduction involves cellular proteins and enzymes that convert a signal to another signal to create a pathway cascade.
The cellular response involves target genes in the nucleus being transcribed and translated to form proteins involved in the production, growth, movement, differentiation, apoptosis, structure, and enzymes.
Dysregulation of cellular signal transduction pathways underlies most of the hallmarks of cancer.
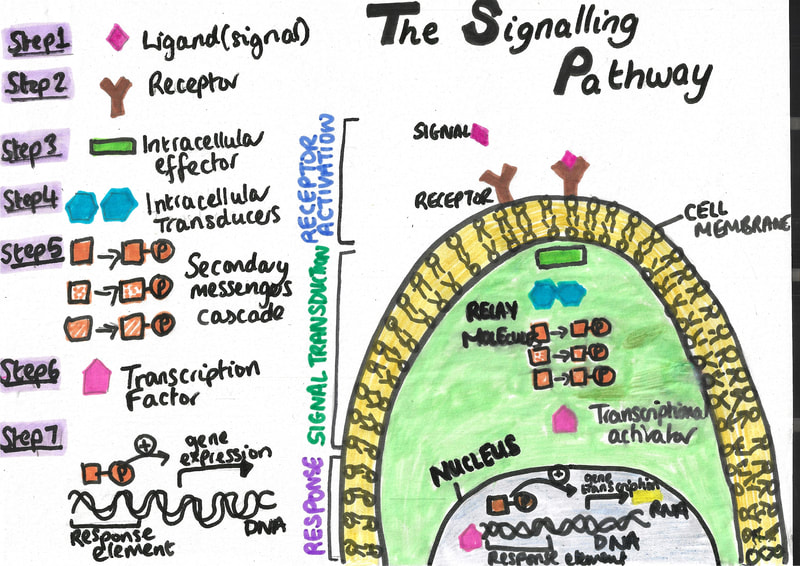
The Signalling Pathway
This image presents key steps involved in the signalling pathway to induce communication between cells. There are three main key steps: receptor activation (navy blue; Steps 1 to 4); Signal transduction (dark green; Step 5 to 6) and cellular response (dark purple; Step 7). A larger size of this image can be found in the resource list.
Resource List For Lecture Three
Youtube Video
Glossary
Quiz
PDF format of the images
Leave a comment