
Lecture Five: Signal Transduction And Cellular Response
This lecture aims to provide insight into the subsequent steps of the cellular process: signal transduction and cellular process. The signal transduction pathway is where the signal is transmitted through the cytoplasm after receptor activation using second messengers that can change the behaviour of proteins. It also requires enzymes activated through phosphorylation (addition of a phosphate group). Additional activity takes place to initiate downstream signaling activity. The four main messengers discussed in the lecture are calcium ions, cyclic AMP (cAMP), Diacylglycerol (DAG), and Inositol triphosphate (IP3). There are different types of transporters and the three revealed are symporters that bind two or more ions /molecules in the same direction. These antiporters bind two or more ions/molecules in the opposite direction and the uniporters bind to a single molecule or ion across the membrane.
The cellular response is dependent on three factors: receptor, signal transduction, and target proteins involved in growth, development, and differentiation. In the lecture, examples are provided of transcription factors that regulate the expression of genes that affect cellular response.
Types Of Secondary Messengers
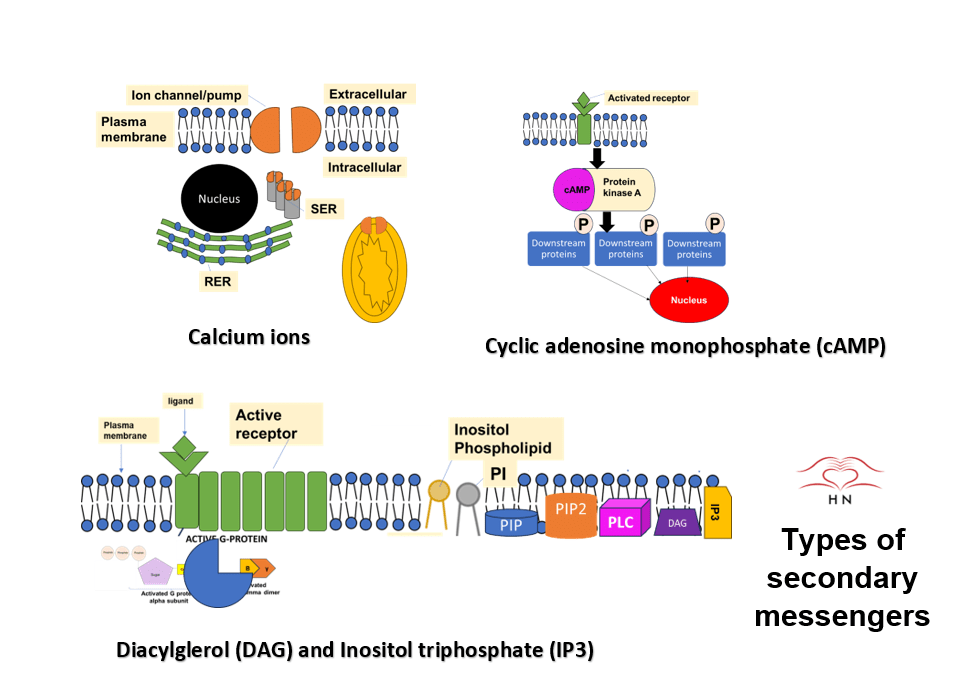
This image presents four main types of secondary messengers: calcium ions, cyclic AMP (cAMP), Inositol triphosphate (IP3), and Diacylglycerol (DAG). Calcium ions are stored in vesicles and are useful in hydrophilic molecules/ligands (water-loving/water-soluble). Calcium ion pumps are found in different structures of the cell, for instance, the cell membrane, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum. The cAMP is produced by the energy source, adenosine triphosphate (ATP) using the enzyme adenyl cyclase. cAMP (fuchsia pink) can bind to the enzyme cAMP-dependent kinase (A-kinase). The activated A-kinase A phosphorylates proteins in the downstream signaling pathway. IP3 is a fat molecule with a carbohydrate (sugar) head (creme). It is produced from a phospholipid called phosphatidylinositol (PI; peach) found in the cell membrane and is near cell surface receptors. PI is phosphorylated to form PI-phosphate (PIP; blue) and PI bisphosphate (PIP2; orange). Phospholipase C (PLC; pink) enzyme cleaves PIP2 to form DAG (purple)and IP3. DAG is involved in phosphorylating downstream targets and IP3 can stimulate calcium ions. A larger size of this image can be found in the resource list.
Resource List For Lecture Five
Youtube Video
Glossary
Quiz
PDF format of image
Leave a comment